Tungsten powder is a dense powder metal valued for its very high melting point, hardness, wear resistance and high-temperature strength. This article provides an overview of tungsten metal powders, manufacturing methods, grades, applications and leading leverancier van wolfraammetaalpoeder.
Overview of Tungsten Metal Powder
Tungsten metal powder, also known as tungsten carbide or simply tungsten powder, is composed of microfine particles of pure elemental tungsten metal or an alloy containing tungsten. Key properties include:
- Extremely high melting point of 3422°C
- Density almost twice that of steel
- Hardness close to diamond
- Excellent wear and erosion resistance
Tungsten powder is available in various grades based on purity, chemistry, particle size distribution and morphology. Custom alloys contain cobalt, nickel, iron or copper to enhance properties.
Tungsten Powder Types
| Type | Beschrijving | Kenmerken |
|---|---|---|
| Zuiver wolfraam | Elemental tungsten 99.9% purity | Highest melting point, density, stiffness |
| Tungsten carbide | Tungsten carbide-cobalt cermet | Extreme hardness and wear resistance |
| Heavy alloys | Tungsten alloys with nickel, copper etc. | High-density ballast applications |
Tungsten Powder Properties
| Eigendom | Zuiver wolfraam | Wolfraamcarbide |
|---|---|---|
| Dichtheid (g/cc) | 19.3 | 15.63 |
| Smeltpunt | 3422°C | 2870°C (decomposes) |
| Mohs hardheid | 7.5 | 8.5-9.5 |
| Sterkte (MPa) | 550 | 700-2000 |
Specificaties van wolfraampoeder
Tungsten powder is available in different particle sizes, size distributions, shapes and purity levels based on the production process and final application requirements.
| Parameter | Bereik |
|---|---|
| Deeltjesgrootte | 0.5 – 15 microns |
| Tik op dichtheid | 3-12 g/cc |
| Schijnbare dichtheid | >50% of true density |
| Puurheid | 99,9% tot 99,995% |
| Zuurstofgehalte | <100 – 1000 ppm |
| Koolstofgehalte | <100 – 500 ppm |

Production Methods for Tungsten Powder
The extreme high temperature properties of tungsten require specialized powder production techniques under inert atmospheres. The main methods include:
1. Waterstofreductie
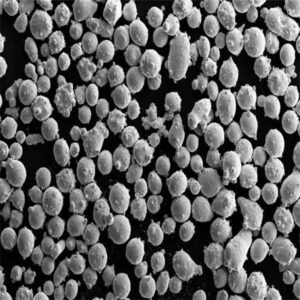
Tungsten ores are reacted with hydrogen gas to produce tungsten powder. It generates irregular angular powders suitable for pressing or additive manufacturing.
2. Thermal Plasma Spheroidization
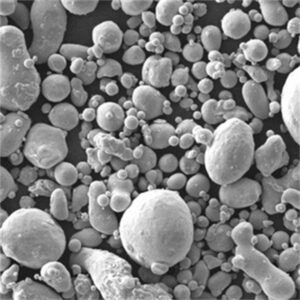
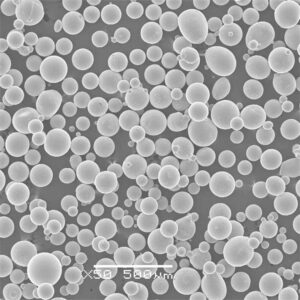
Irregular tungsten powder feedstock is injected into a thermal plasma jet to create fully dense, spherical powders ideal for additive manufacturing, thermal spray, MIM etc.
3. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
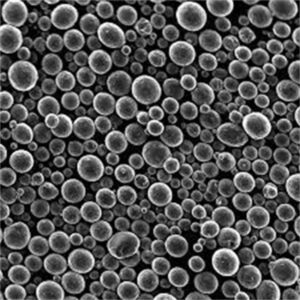
Ultrafine tungsten powders with particle sizes below one micron and high purity levels are produced via tungsten hexafluoride in a CVD reactor.
Tungsten Powder Manufacturing Methods
| Methode | Deeltjesvorm | Solid Density | Maatbereik |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waterstofreductie | Onregelmatig, hoekig | Laag | 1-10 micron |
| Plasma-sferoïdisatie | Bolvormig | Hoog | 10-100 microns |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition | Bolvormig | Medium | 0.05-1 micron |
Applications of Tungsten Metal Powder
The unique properties like high density, hardness, melting point and conductivity make tungsten metal powders suitable for:
Elektronica
- Vibration motor weights
- Mobile device components
- Stralingsafscherming
- Thermisch beheer
Leger en defensie
- Stralingsafscherming
- Kinetic energy penetrators
- Warhead liners
- Aerospace counterweights
Automobiel
- Tire studs
- Engine and drivetrain components
Energie
- Nuclear fuel pellets
- Elektrische contacten
Productie
- Wear resistant tooling
- Ovenonderdelen voor hoge temperaturen
Additieve productie
- Warmteafvoeren
- Stralingsafscherming
- Aerospace and motorsports
Wereldwijd leverancier van wolfraammetaalpoeder
The complex production and hazardous handling requirements mean only a few specialist producers manufacture tungsten metal powders globally.
Leading tungsten powder suppliers include:
Buffelwolfraam
Founded: 1931
Headquarters: Depew, New York USA
- Products: Tungsten powders, parts, and wires
- Production capacity: Not disclosed
- Markets served: Aerospace, medical, electronics, lighting
HC Starck Tungsten Powders
Founded: 1966
Headquarters: Munich, Germany
- Products: Pure tungsten, tungsten carbide, tungsten alloys
- Production capacity: Largest western producer
- Markets served: Automotive, manufacturing, oil and gas, chemicals
Global Tungsten & Powders
Founded: 1997 from Teledyne group
Headquarters: Towanda, Pennsylvania USA
- Products: Pure tungsten, tungsten oxide powders
- Production capacity: Not disclosed
- Markets served: Electronics, lighting, aviation, medical
GuangDong XiangLu Tungsten
Founded: 1997
Headquarters: Ganzhou, China
- Products: Tungsten powder and tungsten products
- Production capacity: Leading Chinese supplier
- Markets served: Automotive, construction, industrial
H.C. Starck-oplossingen
Founded: 1966 as subsidiary of H.C. Starck Group
Headquarters: Newton, Massachusetts USA
- Products: Refractory metal powders including tungsten
- Production capacity: Range of atomizer sizes
- Markets served: Electronics, industrial, medical
Midwest wolfraam service
Founded: 1983
Headquarters: Willowbrook, Illinois USA
- Products: Tungsten alloys and heavy metal blends
- Production capacity: Small batches
- Markets served: Defense, aviation, energy, motorsports
Nippon Tungsten Co. Ltd
Founded: 1936
Headquarters: Toyama, Japan
- Products: Tungsten powder and mill products
- Production capacity: Not disclosed
- Markets served: Japanese domestic manufacturing
Plansee
Founded: 1921
Headquarters: Reutte, Austria
- Products: Molybdenum, tungsten mill products and powders
- Production capacity: Leading global consolidator
- Markets served: Electronics, lighting, medical, industrial
Tungsten Powder Pricing
| Leverancier | Product | Deeltjesgrootte | Prijs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buffelwolfraam | Zuiver wolfraam | 1-10 micron | $50/lb |
| HC Starck | Tungsten carbide | 0.5-3 microns | $50/lb |
| Global Tungsten | Zuiver wolfraam | 1 micron | $175/kg |
| XiangLu Tungsten | Wolfraam poeder | 1-10 micron | $30/kg |
Tungsten and tungsten carbide powders demand premium pricing due to hazardous production methods and specialized applications. Significant volume discounts apply.
kiezen leverancier van wolfraammetaalpoeder
Key factors in selecting a tungsten powder vendor:
Technische expertise
- Experience handling refractory metal powders
- Staff scientists and engineers that understand applications
- Ability to customize alloys and particles
Kwaliteit en consistentie
- Stringent quality control procedures
- Documentation and certifications
- Ensure batch-to-batch repeatability
Inventaris
- Quickly ship common grades from stock
- Minimum order quantities may apply
Prijzen
- Typical $50-175 per kg for powder
- Larger quantities receive discounted pricing
Hazmat Compliance
- Tungsten powder shipments require DG classification
- Proper labeling, containment and paperwork
Work closely with prospective suppliers and get test samples before committing to understand their capabilities fully.
Tungsten vs. Alternative Powder Metals
Tungsten vs. Tantalum
Similar high melting point but tungsten is harder and has higher wear resistance. Tantalum more ductile and expensive due to rarity. Both used in electronics and alloying applications.
Tungsten vs. Lead
Lead cheaper but toxic while tungsten eco-friendly alternative for weighting applications. Higher strength lead alloys approach tungsten in density. Lead melts easily unlike tungsten’s extreme resistance.
Tungsten vs. Gold
Gold extremely expensive precious metal. Tungsten used since WW1 as heavy substitute for gold electroplating in counterfeiting coins. Similar density allows tungsten to mimic the feel of gold.
Tungsten vs. Depleted Uranium
Depleted uranium ~40% denser but low-level radioactivity limits applications. Tungsten suitable non-hazardous alternative for radiation shielding and defense uses. Cheaper, easier to handle.
Tungsten vs. Platinum
Platinum higher melting point than tungsten but costs thousands per ounce. Tungsten an affordable substitute for high-temperature electrical contacts to replace costly platinum group metals.

FAQ
Q: What is the difference between tungsten metal powder and tungsten carbide powder?
A: Pure tungsten metal powder is elemental tungsten whereas cemented tungsten carbide is a composite of tungsten carbide particles bonded together by cobalt. Carbide grades focus on extreme hardness.
Q: What hazards are associated with tungsten powder handling?
A: Tungsten fine powder can combust spontaneously in air forming explosive mixtures. Strict inert atmosphere protocols are mandatory. Water contact produces volatile hydrogen gas. Respirators required to prevent lung tissue damage.
Q: What particle size tungsten powder is best suited for additive manufacturing?
A: For binder jetting processes, fine tungsten powder from 5-50 microns with spherical morphology and high powder flow is ideal. For laser-based printers, 10-100+ micron powder is commonly used.
Q: What postprocessing is used on additively manufactured tungsten parts?
A: Sintering followed by hot isostatic pressing (HIP) helps achieve maximum density and uniform fine-grained microstructure. Additional heat treatments, machining and finishing may be used per application requirements.
Q: How are tungsten and its alloys joined to other components?
A: Brazing is commonly used to join tungsten parts using silver-based and copper-based alloys. Diffusion bonding and adhesive bonding are alternate methods. Welding requires specialized techniques due to contamination concerns.