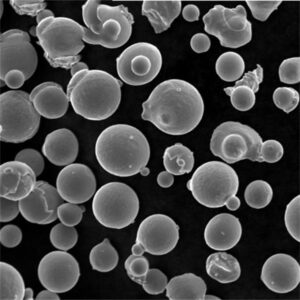
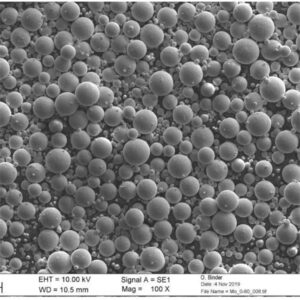
Overview of molybdenum titanium powders
molybdeen titaanpoeder refer to fine metallic particles of each element produced through atomization processes. They display high strength, hardness and heat resistance.
The powders are used individually or as blends for manufacturing high performance alloys. Their controlled particle size distribution allows complex near-net shape components to be built up from layers during metal 3D printing.
Some key characteristics of molybdenum and titanium powders:
Molybdeen Poeder
- Excellent creep resistance and stability at high temperatures
- Lage thermische uitzettingscoëfficiënt
- Hoge hardheid en slijtvastheid
- Used as alloying addition to strengthen steels and superalloys
Titanium Poeder
- Extremely strong yet lightweight as a structural metal
- Uitstekende corrosieweerstand
- Biocompatibel voor medische implantaten
- Reactief en vereist gecontroleerde verwerking
Blended/Alloyed Powders
- Combine beneficial properties of each element
- Allows customized material performance
- Requires optimized 3D printing parameters
By manipulating compositions through AM, innovative alloys with superior properties suited for extreme environments can be created.

Types of Molybdenum and Titanium Powders
Molybdenum and titanium powders are commercially available in various types for metal additive manufacturing:
| Powder Variant | Kenmerken | Typische toepassingen |
|---|---|---|
| Molybdeen | Pure and alloyed grades | AM of moly alloys, catalysts |
| Titaan Ti-6Al-4V | Aerospace alloy | Load-bearing aerostructures |
| Titanium Ti-6Al-7Nb | Biocompatible alpha-beta alloy | Medical implants, prosthetics |
| Mo-Ti elemental blends | Custom alloy compositions | Advanced engineering applications |
| Mo-Ti master alloys | Pre-alloyed blends | Simplified AM processing |
In their elemental form, molybdenum provides high temperature hardness while titanium contributes strength and corrosion resistance. By combining both through AM, innovative alloys can be created with enhanced overall performance.
Composition/Alloying
Molybdenum and titanium powders have the following nominal compositions:
Molybdeen Poeder
| Element | Samenstelling bereik |
|---|---|
| Molybdeen (Mo) | 99% and above |
| Zuurstof (O) | Maximaal 0,01% |
| Koolstof (C) | Maximaal 0,01% |
| Ijzer (Fe) | Maximaal 0,01% |
| Other metals | Maximaal 0,01% |
High purity is required for reproducibility during AM and downstream processing. Contamination can adversely affect material properties.
Titaan Ti-6Al-4V
| Element | Gewicht % |
|---|---|
| Titaan (Ti) | Evenwicht |
| Aluminium (Al) | 5.5-6.75 |
| Vanadium (V) | 3.5-4.5 |
| Ijzer (Fe) | < 0.3 |
| Zuurstof (O) | <0.2 |
| Other metals | <0,1 |
Small amounts of alloying additions of aluminum and vanadium significantly enhance titanium’s strength for load-bearing lightweight structures.
For blended Mo-Ti powders, the relative ratios can be varied from 100% Mo to 100% Ti to create customized alloys. Using both elemental and pre-alloyed blended powders, the unlimited freedom of compositions allows hitherto unexplored alloys to be developed through AM.
Eigenschappen van molybdeen titaanpoeder
Molybdeen Poeder
| Fysieke eigenschappen | |
|---|---|
| Dikte | 10,22 g/cm3 |
| Smeltpunt | 2610°C |
| Warmtegeleiding | 138 W/mK |
| Elektrische weerstand | 5.5 μΩ-cm |
| Uitzettingscoëfficiënt | 5.3 μm/m-°C |
| Mechanische eigenschappen | |
|---|---|
| Hardheid | ~300 HV |
| Ultieme treksterkte | 600-800 MPa |
| Opbrengststerkte (0,2% offset) | 500+ MPa |
| Verlenging | 30-50% |
| Elasticiteitsmodulus | 325 GPa |
Molybdenum powder enables extremely hard and heat resistant alloys to be fabricated using AM techniques. Parts maintain high strength in oxidizing, corrosive and frictional wear conditions at elevated temperatures exceeding 1000°C.
Titanium Ti-6Al-4V Powder
| Fysieke eigenschappen | Waarden |
|---|---|
| Dikte | 4,43 g/cm3 |
| Smeltpunt | 1604-1660°C |
| Warmtegeleiding | 7.2 W/mK |
| Elektrische weerstand | 170 μΩ-cm |
| Coeff. of Thermal Expansion | 8.6 μm/m-°C |
| Mechanische eigenschappen | As Built | Gegloeid |
|---|---|---|
| Treksterkte | 1050 MPa | 950 MPa |
| Opbrengststerkte (0,2% offset) | 900 MPa | 850 MPa |
| Verlenging | ~15% | ~20% |
| Hardheid | ~350 HV | ~300 HV |
The fine balance of high strength along with decent ductility makes this an extremely popular aerospace alloy for critical printed parts in rocket engines, airframes and turbines.
By blending molybdenum and titanium powders in different ratios, a combination of their properties can be realized in customized alloys.
Toepassingen
Molybdenum and titanium powders enable high performance metal AM parts tailored to extreme environments:
Olie en gas
- Fracking pumps and valves exposed to abrasive fluids at high pressures and temperatures
- Corrosion resistant piping for oil well acids, gases and brines
Lucht- en ruimtevaart
- Aircraft turbine blades and vanes operating at >1000°C for improved fuel efficiency
- Lightweight airframe and engine brackets with enhanced specific strength
Automobiel
- Connecting rods, drive shafts and chassis components reducing weight
- Friction stir welding tools for fabricated body panels
Medisch
- Orthopedic implants with bone-like elastic modulus
- Corrosion resistant bio-interactive devices
Industrieel
- Lightweight robot arms with improved strength-to-weight ratio
- Dimensionally stable power generation hardware
By overcoming limits of conventional processing, AM with molybdenum and titanium enables next-gen high performance structures. Parts show marked gains in service performance under thermal, mechanical and chemical stresses.
Specifications of molybdenum titanium powders
Molybdenum and titanium powders must meet exact chemistry requirements and stringent quality specifications for additive manufacturing use per industry accepted standards:
Chemical Purity Standards
| Poederkwaliteit | Standaard |
|---|---|
| Molybdeen | ASTM B393 |
| Titaan Ti-6Al-4V | ASTM F2924 |
| Titanium Ti-6Al-7Nb | ASTM F3001 |
Typical Powder Characteristics
| Attribuut | Vereisten | Testmethoden |
|---|---|---|
| Deeltjesvorm | Overwegend bolvormig | SEM imaging per ASTM B822 |
| Schijnbare dichtheid | 2 to 5 g/cc | MPIF 04 or ASTM B212 |
| Stroomsnelheid | >30 sec for Hall flow test | ASTM B213 |
| Deeltjesgrootteverdeling | D10, D50, D90 optimized for AM process | ASTM B822 |
| Loss on ignition (LOI) | Low oxygen/nitrogen | Analyse van inertgasfusie |
| Microstructuur | Defect-free, no satellites | SEM at high magnifications |
The requirements aim to ensure uniform melting behavior, defect-free builds and reproducible end part properties.
Wereldwijde leveranciers
Many established manufacturers provide molybdenum and titanium powders for AM applications:
Molybdeen Poeder
| Bedrijf | Merknamen | Productie methode |
|---|---|---|
| H.C. Starck | ma | Elektrolytisch |
| Molymet | PureMo | Waterstofreductie |
| Plansee | MolyPowder | Calcium reduction |
| Wolfraam uit het Middenwesten | TeroMoly | Calcium reduction |
Titanium Poeder
| Bedrijf | Aangeboden rangen | Productie methodes |
|---|---|---|
| AP&C | Ti-6Al-4V, Other Ti Alloys | Plasma-verneveling |
| Timmerman additief | Ti-6Al-4V | Plasma-verneveling |
| Sandvik | Ti6Al4V ELI, Ti6Al4V ELI-0406 | Plasma-verneveling |
| Tekna | Ti-6Al-4V, Ti 6Al-7Nb | Plasma-verneveling |
| TLS-techniek | Ti6Al4V, Ti6Al4V ELI, Ti Grade 23 | Gas, plasma atomization |
Zowel gevestigde metaalpoederproducenten als gespecialiseerde AM-poederfabrikanten leveren deze materialen volgens veeleisende industriespecificaties.
Prijzen van molybdeen titaanpoeder
Als veelgebruikte materialen in metal AM zijn er gepubliceerde prijsindicatoren voor molybdeen- en titaanpoeders beschikbaar:
Molybdeen Poeder
| Deeltjesgrootte | Prijsbereik |
|---|---|
| 10-45 µm | $40 - $60 per kg |
| 15-53 μm | $50 - $70 per kg |
| Aangepaste maten | > $100 per kg |
Titanium Ti-6Al-4V Powder
| Deeltjesgrootte | Prijsbereik |
|---|---|
| 15-45 µm | $150 - $450 per kg |
| 45-100 μm | $100 - $350 per kg |
| Aangepaste maten | > $500 per kg |
Prijzen zijn afhankelijk van de kwaliteitsklasse, lotgrootte, distributiebereik, plasma vs. gasverstuiving en inkoopvolume. Prijzen voor grote hoeveelheden en contracten worden meestal rechtstreeks met de leveranciers onderhandeld.
Voor- en nadelen van molybdeen- en titaniumlegeringen uit AM
Pluspunten
- Uitstekende prestaties bij hoge temperaturen
- Verbeterde specifieke sterkte en stijfheid
- Veerkrachtig bij thermische en vermoeidheidsbelasting
- Complexe koelkanalen integreren kracht en warmteoverdracht
- Geconsolideerde assemblages verlagen het aantal onderdelen
- Kortere ontwikkelingstijden in vergelijking met gietstukken
- Aangepaste legeringen met samenstellingen op maat
- Reactieve materialen verwerkt zonder verontreiniging
Nadelen
- Hogere kosten dan standaardlegeringen
- Uitdagende printbaarheid dicteert strenge parameteroptimalisatie
- Nabewerking kan nodig zijn om de uiteindelijke eigenschappen te verkrijgen
- Anisotropie van opbouw in lagen
- Gebrek aan ontwerp- en materiaalstandaarden
- Reactieve poeders vereisen gecontroleerde opslag en hantering
Dankzij voortdurend onderzoek en kwalificatie kunnen molybdeen en titanium dankzij metaal-AM hun potentieel waarmaken bij het ontwerpen van lichtere en sterkere structuren met hoge prestaties.
Hoe worden molybdeen- en titaniumpoeders gemaakt?
Geavanceerde gasatomisatieprocessen produceren de fijne metaalpoeders met nauwkeurige controle over kritieke kenmerken zoals deeltjesvorm, groottebereik en chemische zuiverheid.
Gasverstuiving
Hoogzuivere ingots worden inductief gesmolten in een inerte atmosfeer en de vloeibare metaalstroom wordt in gespecialiseerde verstuivingsvaten gegoten. Krachtige argon- of stikstofgasstralen verstuiven het metaal in fijne druppeltjes die snel stollen tot poeder.
Door de gasstroomparameters en koelsnelheden te optimaliseren, worden bolvormige deeltjes met de gewenste deeltjesgrootteverdeling verkregen. Het poeder wordt vervolgens gezeefd in verschillende grootteklassen die nodig zijn voor verschillende AM-processen.
Extra verwerking
Er kunnen verdere stappen worden ondernomen om de poedereigenschappen te verbeteren: ontgassen om het zuurstofgehalte te verlagen, gloeien om de interne spanningen als gevolg van snelle stolling te verminderen en mengen met andere poederfracties om specifieke afmetingen te verkrijgen.
De poeders worden uiteindelijk verpakt onder inerte atmosfeer om oxidatie te voorkomen voordat ze naar de klant worden verzonden. Behandelings- en opslagprotocollen voorkomen vochtabsorptie of besmetting tijdens downstream metaal AM-verwerking.
Binder Jetting vs. poederbedfusie van molybdeen en titanium
Molybdeen- en titaanlegeringen kunnen worden geprint met zowel binder jetting als poederbedfusie:
| Aspect | Binder jetting | Poederbedfusie |
|---|---|---|
| Bouwmethode | Vloeibare bindmiddelen | Laser/e-beam smelten |
| Resolutie | ~100 μm | ~50 μm |
| Porositeit | Hoger, vereist infiltratie | Lager, dichtheid 99%+ |
| Oppervlakteafwerking | Ruw, moet bewerkt worden | Matig, moet mogelijk worden afgewerkt |
| Mechanische eigenschappen | Laag, varieert door deel | Hoger, meer uniform |
| Dimensionale nauwkeurigheid | ±0.3% met krimp | ±0,1% of beter |
| Nabewerking | Debinding, sintering, HIP | Support removal, heat treatment |
| Bouwgrootte | Industrial scale | Smaller chambers |
| Time Requirements | Dagen | Hours up to 1-2 days |
| Economics | Lower part cost, higher volume | Lower volume, expensive hardware |
Binder jetting is suitable for design concept models due to speed and low cost. Powder bed fusion creates high fidelity end use parts with superior properties.

Molybdenum Titanium Alloys – Prospects
Molybdenum and titanium are desirable individually for their high temperature capabilities and strength-to-weight ratio respectively. By combining both elements, AM unlocks unique alloy compositions with tailorable properties.
Potential Alloy Groups
- Mo-Ti intermetallics for ultra-high temperature strength
- Mo-Ti silicides with oxidation resistance above 1500°C
- Mo-Ti borides with extreme hardness at high temperatures
- Mo-Ti carbides matching ceramic hardness levels
These advanced materials overcome barriers with traditional processing through composition control and microstructure manipulation made possible using metal AM processes.
Target Applications
- Hypersonic aerospace vehicles and re-entry structures
- Next generation jet turbine and rocket engine hot section parts with doubled operating temperatures
- Lightweight automotive powerplants with high exhaust temperatures
- Nuclear reactor internals continuously working in intensely radioactive high heat fluxes
- Industrial furnace heating elements and fixtures boosting temperatures and efficiency
Additive manufacturing removes the constraints around molybdenum and titanium, opening up new horizons for extreme environment and high performance applications.
Veelgestelde vragen
Q: What is molybdenum used for?
A: With excellent high temperature properties, molybdenum sees major use as an alloying addition to strengthen heat-resistant steels and superalloys used in aerospace, power generation, furnace construction, missile components among other demanding applications.
Q: Is molybdenum toxic?
A: Elemental molybdenum and its alloys generally have low toxicity levels and are safe for engineering use. However, some molybdenum compounds when inhaled over long durations may have potential carcinogenic effects warranting protective equipment use during handling and machining.
Q: Is titanium expensive?
A: Titanium alloys display a higher raw material cost compared to steels and aluminum alloys. However, with buy-to-fly ratios approaching 1 for AM manufacture, finished titanium part costs can be economical for industries like aerospace willing to adopt new technologies and designs.
Q: What makes titanium ideal for implants?
A: The biocompatibility of titanium alloys coupled with their high strength-to-weight ratio makes them ideal for replacing human bone. The modulus of elasticity can be reduced closer to that of bone by alloying with biocompatible beta stabilizers like Nb and Ta for improved life of load-bearing implants.
Q: Which 3D printing process is used for molybdenum and titanium?
A: For high-performance end-use parts, powder bed fusion techniques like selective laser melting (SLM) and electron beam melting (EBM) are predominantly used. The high temperature heat source achieves near full density builds with superior properties suited for engineering applications.
Q: Why blend molybdenum with titanium powder?
A: Molybdenum enhances high temperature hardness, creep resistance and tool steel-like properties while titanium contributes excellent corrosion resistance and low density attributes. Together, customized alloys made by directly blending their powders using AM provide the ideal combination for advanced applications.