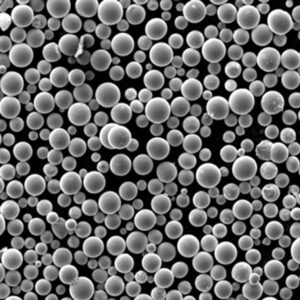
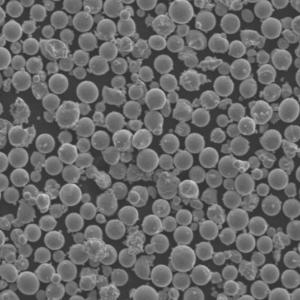
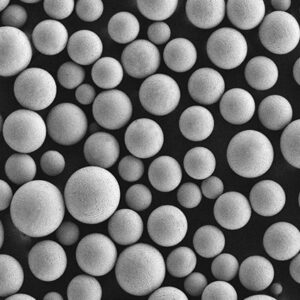
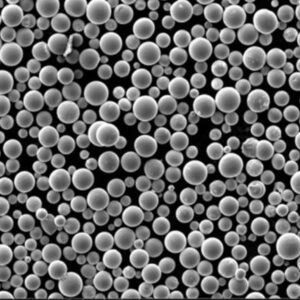
Verneveling van metaalpoeder is a critical technology for producing fine metallic powders with specialized characteristics. This guide covers the fundamentals, methods, applications and commercial landscape of metal powder atomization.
What is Metal Powder Atomization?
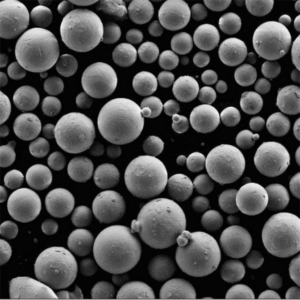
Metal powder atomization refers to industrial processes that turn molten metal alloys into fine liquid droplets, rapidly solidifying them into powder particles.
It involves:
- Melting metals into a liquid state
- Generating a molten metal stream
- Breaking up the metal into discrete droplets
- Solidifying the droplets into powder
- Collecting and sieving the powder
Atomization is used to produce metal powders with unique compositions, sizes, shapes and microstructures suitable for advanced applications.
Key Atomization Benefits
- Custom alloy compositions
- Controlled particle sizes
- Spherical powder shapes
- Defect-free powder metallurgy
- Novel microstructures
- Custom powder properties
Common materials made through atomization include various alloy systems:
- Roestvrij staal
- Gereedschapsstaal
- Kobaltlegeringen
- Nikkel legeringen
- Titanium legeringen
- Wolfraam legeringen
- Edelmetalen

Metal Powder Atomization Methods
There are 5 main commercial atomization techniques:
Gasverstuiving
- Uses pressurized inert gas jets
- Common gases: Nitrogen, Argon, Helium
- Produces spherical, smooth powders
Waterverneveling
- Uses high pressure water jets
- Lower cooling rates than gas
- Irregular powder shapes
Centrifugale verneveling
- Molten metal poured on spinning disc
- Economical powder production
- Medium cooling rates
Ultrasone verstuiving
- Uses ultrasonic vibrations
- Specialized lab-scale method
- Nanoparticle production
Electrode Induction Melting
- Electrode vaporization in inert gas
- Limited niche applications
- Lower productivity
Atomization Method Comparison
| Methode | Deeltjesvorm | Maatbereik | Productiviteit | Kosten |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gasverstuiving | Bolvormig | 10-150 µm | Hoog | Hoog |
| Waterverneveling | Onregelmatig | 20-400 μm | Heel hoog | Laag |
| Centrifugale verneveling | Semi-spherical | 20-250 μm | Medium | Medium |
| Ultrasone verstuiving | Bolvormig | 1-100 nm | Zeer laag | Hoog |
| Electrode Induction Melting | Mixed | 10-100 µm | Laag | Medium |
Verstuiving van metaalpoeder Proces
Commercial metal powder atomization involves a series of tightly controlled steps under inert atmosphere:
1. Raw Material Selection
- Pure metals or master alloys
2. Melting
- Vacuum induction melting up to 2000°C
- Precise alloy chemistry inputs
3. Atomization
- Pouring molten metal into atomizing zone
- Breaking up metal stream into droplets
- Quenching and solidifying droplets
4. Powder Collection
- Settling chamber to collect powder
- Cycloonafscheiders
5. Sieving
- Classifying powder into size fractions
- Further annealing if needed
6. Quality Control
- Sampling and testing per standards
- Packaging and shipment
The production environment must have no oxygen or moisture contamination. Operational parameters like temperature profiles, gas pressures and flow dynamics are closely monitored.
Metal Powder Atomization Applications
Some major applications taking advantage of atomized metal powder include:
Additieve productie
- Selectief lasersmelten
- Binder spuiten
- Het smelten van elektronenbundels
Metaal spuitgieten
Thermische spuitcoatings
Heet isostatisch persen
Brazing Materials
Katalysatoren
Poeder-Metallurgie
- Pers- en sintergereedschap
- Hoogwaardige onderdelen
- Porous structures
- Soft magnetic composites
Atomized powder enables emerging technologies like additive manufacturing across industries:
| Industrie | Toepassingen | Voordelen |
|---|---|---|
| Lucht- en ruimtevaart | Turbine blades, impellers, airframe components | Hoge sterkte-gewichtsverhouding |
| Automobiel | Gears, connecting rods, chassis parts | Increased efficiency |
| Medisch | Joint replacements, implants, precision tools | Biocompatibiliteit |
| Elektronica | Shielding, contacts, sensors | Enhanced performance |
| Olie gas | Gereedschappen in het boorgat, kleppen | Wear and corrosion resistance |
Metal Powder Atomization Materials
Many alloy systems and material types are processed through atomization:
Roestvrij staal
- Austenitic grades like 304, 316, 317
- Ferritic and martensitic grades
- Custom compositions available
Gereedschapsstaal
- H13, P20, D2, M2 grades
- Hoge slijtvastheid
- High hardness after heat treatment
Kobaltlegeringen
- Biomedical CoCrMo alloys
- Wear resistant StelliteTM alloys
Nikkellegeringen
- Corrosion resistant alloys like Inconel 625
- Heat resistant superalloys
Titanium legeringen
- Ti6Al4V grade 5 titanium
- Commercially pure titanium
Vuurvaste metalen
- Niobium, molybdenum, tungsten
- Very high melting points
Metal Powder Atomization: Specifications
Critical specifications for atomized metal powders include:
Deeltjesgrootteverdeling
- Typically 10 to 150 microns
- Application method dictates ideal size
- Sieving classifies desired fractions
Deeltjesvorm
- Spherical, smooth morphologies
- Impact compaction, flowability
Scheikunde
- Precisely blended compositions
- Custom alloys designed for properties
Dikte
- Up to 98% theoretical density
- Density optimization modeling
Oppervlakte
- Relatively high surface area
- Impacts reactivity, solubility
Microstructuur
- Controlled grain sizes and phases
- Rapid solidification dynamics
| Parameter | Betekenis | Measurement Technique |
|---|---|---|
| Deeltjesgrootteverdeling | Controls downstream processability | Deeltjesgrootteanalysator met laserdiffractie |
| Deeltjesvorm | Impacts density and flow behavior | Scanning-elektronenmicroscopie |
| Scheikunde | Achieves target material performance | Optical emission spectrometry, ICP mass spectroscopy |
| Dikte | Related to achievable properties | Gas pycnometry, apparent density tester |
| Oppervlakte | Affects reactivity and solubility | Gas absorption surface area analyzer |
| Microstructuur | Bepaalt mechanische eigenschappen | X-ray diffraction, metallography |
Metal Powder Atomization Cost Analysis
Atomized metal powder is more expensive than conventional raw materials due to specialized processing:
- Small batch production
- Complex quality control
- Manual handling steps
- Equipment maintenance
- Consumables and energy
- R&D expense recovery
Cost Drivers:
- Feedstock metal costs
- Quality conformance
- Order size
- Deeltjesgrootte
- Exotic alloys
Economics:
- Raw materials: 30% of total cost
- Processing: 70% of total cost
Prijsklassen:
| Materiaal | Prijs per kilo |
|---|---|
| Roestvrij staal | $20-$250 |
| Gereedschapsstaal | $25-$150 |
| Titanium legeringen | $70-$1000 |
| Kobaltlegeringen | $100-$500 |
| Nikkellegeringen | $100-$2000 |
| Tungsten Alloys | $800-$5000 |
Business viability relies on maximizing production capacity utilization and end-to-end yield.
Verstuiving van metaalpoeder: Pros vs Cons
Benefits of Metal Powder Atomization
- Excellent flow characteristics
- Narrow particle size distribution
- Customizable alloy compositions
- Spherical powder shape possible
- Gecontroleerde microstructuren
- Enables emerging technologies
Challenges of Metal Powder Atomization
- High production cost
- Limited batch sizes
- Stringent safety precautions
- Complex quality conformance
- Qualified operator experience vital
- Costly trial-and-error development
- Handling fine reactive powders
Advancements continue expanding the horizons for specialty materials made via atomization.

Veelgestelde vragen
Q: How are metal powders atomized?
A: Metal powders are atomized by breaking up a molten metal stream into fine droplets using gas jets, water jets or centrifugal forces, rapidly solidifying them into powder.
Q: What is water atomization?
A: In water atomization, a thin stream of molten metal alloy is struck by high-pressure water jets which break it up into small droplets. The droplets solidify into irregularly shaped powder particles as they fall through the water.
Vraag: Welke metalen kunnen tot poeders worden verneveld?
A: Many engineering metals like tool steels, stainless steels, nickel alloys, titanium alloys, tungsten alloys and precious metals can be atomized into fine spherical powders or irregular powders using appropriate techniques.
Q: What particle sizes can metal powder atomization achieve?
A: Conventional metal powder atomization can produce powders from around 10 microns to over 150 microns. Specialized nozzles and processing conditions allow particle sizes below 5 microns.
Q: How much does metal powder atomization cost?
A: Due to small volumes and specialized equipment, atomized metal powder costs between 5x to 10x more than standard raw metal stock per unit weight, with pricing ranging from $50 per kg to over $2000 per kg depending on composition and quality.
Q: Can you atomize multiple metals simultaneously into an alloy?
A: Yes, atomization allows melting and alloying various metals into customized compositions which solidify into an alloy powder with the desired elemental ratios and advanced metallurgical properties.
Q: What hazards are associated with metal powder atomization?
A: Fine metal powders may spontaneously combust, explode or be toxic if inhaled. Strict safety protocols for inert gas purging, explosion proof electrical equipment, pressurized nozzles, emergency ventilation and operator PPE are enforced.
Q: What machines are used in metal powder atomization?
A: The main metal powder atomization equipment includes vacuum induction furnaces, tundish pouring systems, gas and water jet nozzles, atomizing towers, cyclone separators, screening machines, powder drying ovens and sieving station.
Conclusie
Metal powder atomization is an intricate, multi-faceted manufacturing technique essential for new material development crossing industry boundaries. Persistent metallurgical challenges continue driving process refinements through extensive tribology research and plant trials. With broader collaboration across the metal powder value chain harnessing latest automation technologies, atomization promises to elevate manufacturing—not eliminate it.