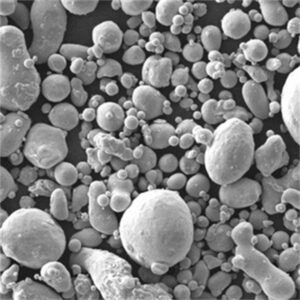
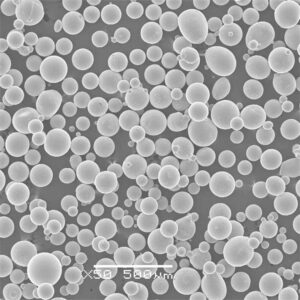
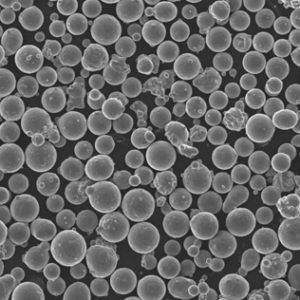
High purity metal powders refer to metallic powders with extremely low levels of impurities, often 99.9% pure or higher. They are utilized across a wide range of advanced applications where contamination-free materials are critical for performance and reliability.
Overview of High Purity Metal Powders
High purity metal powders possess unique properties that make them indispensable for sophisticated technologies. This guide covers key aspects of these powders:
Table 1: Overview of high purity metal powders
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Common metals used | Nickel, cobalt, copper, iron, titanium, tungsten, molybdenum, tantalum, rhenium |
| Zuiverheidsniveaus | 99.9% to 99.999%+ |
| Deeltjesgroottes | Sub-micron to 100 microns |
| Production methods | Vacuum induction melting, gas atomization, chemical reduction |
| Key applications | Electronics, optics, medical devices, aerospace components, additive manufacturing |
| Voordelen | Enhanced performance, reliability, precision |
| Uitdagingen | High production costs, contamination risks |

Types van Hoogzuivere metaalpoeders
Various metals are processed into ultra-high purity powder forms to serve niche applications:
Table 2: Major types of high purity metal powders
| Metal Type | Beschrijving | Toepassingen |
|---|---|---|
| Nikkel | Corrosion-resistant, ductile | Electronics, alloys, batteries |
| Kobalt | Hoge sterkte, biocompatibel | Cutting tools, magnets, medical |
| Koper | High thermal/electrical conductivity | Electronics, thermal management |
| Ijzer | Magnetische eigenschappen | Motors, transformers |
| Titanium | Extremely strong, light | Lucht- en ruimtevaartcomponenten |
| Wolfraam | Very dense, heat/wear-resistant | Radiation shielding, lighting, tools |
| Molybdeen | Behoudt sterkte bij hoge temperaturen | Filaments, rocket nozzles |
| Tantaal | Highly conductive and corrosion-resistant | Capacitors, implants |
| Rhenium | Extremely heat/wear/corrosion resistant | Superalloys, thermocouples |
High purity metal powders exhibit enhanced properties vital for state-of-the-art technologies.
High Purity Metal Powder Production Methods
Stringent protocols minimize contamination in specialized metal powder production facilities:
Table 3: Overview of production methods for high purity metal powders
| Methode | Beschrijving | Deeltjesgroottes | Purity Levels |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vacuüm-inductie smelten | Metal heated in a crucible under high vacuum | 50μm to 150μm | Up to 99.999% |
| Gasverstuiving | Molten metal stream disintegrated by inert gas jets | 5μm to 150μm | Tot 99,9% |
| Chemische reductie | Metal extracted from aqueous solutions/slurries | Sub-micron to 5μm | 99% to 99.9%+ |
Each process can yield ultra-high purity powders tailored for target applications.
Vacuum induction melting uses Skull Crucibles to ensure minimal contact with impurities during heating. High velocity inert gas jets break up molten metal into fine droplets in gas atomization. Chemical reduction precipitates purified metallic particles from chemical solutions.
Stringent protocols in state-of-the-art facilities produce contamination-free ultra-high purity metal powders.
Applications and Benefits of High Purity Metal Powders
The unique properties of contamination-free metal powders serve critical needs in various spheres:
Table 4: Key application areas for high purity metal powders
| Industrie | Toepassingen | Desired Properties | Voordelen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elektronica | Conductors, capacitors, circuits, microchips | High conductivity, low resistance | Miniaturization, fast processing speeds |
| Lucht- en ruimtevaart | Jet engine and airframe components | Strength under extreme conditions | Lighter and efficient structures |
| Medische apparaten | Implants, imaging agents, radiation shielding | Biocompatibility, corrosion resistance | Improved body acceptance, precise visualization |
| Optiek | Telescopes, microscopes, lasers | Extreme surface precision | Sharper resolution and focus |
| Additieve productie | 3D printed critical components | Reliable material properties | Design freedom, rapid prototyping |
Stringent quality demands of cutting-edge technologies fuel the need for contamination-free high purity metal powders.
High Purity Metal Powder Suppliers
High purity powder metallurgy is an extremely specialized field with only a few major global producers having the expertise and infrastructure for quality powder manufacturing:
Table 5: Leading suppliers of high purity metal powders
| Bedrijf | Markets Served | Metals Offered | Deeltjesgroottes | Purity Levels |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BASF | Aerospace, medical, optics | Nickel, cobalt | 15μm to 150μm | Up to 99.995% |
| Sandvik | Additive manufacturing, automotive | Nickel, cobalt, titanium | 10μm to 45μm | Tot 99,9% |
| AMETEK | Elektronica, defensie | Tungsten, molybdenum | 0.5μm to 10μm | Up to 99.999% |
| Jien Nikkel | Alloys, batteries | Nickel, copper | Up to 100μm | Up to 99.99% |
| Atlantische apparatuuringenieurs | R&D, universities | Nickel, iron, copper | Up to 325 mesh | Up to 99.9%+ |
Leading metal powder producers offer tailored ultra-high purity solutions to niche industries.
Carefully vet suppliers based on application needs and rigor of quality assurance protocols. Materials must adhere to strict cleanliness standards.
Choosing Right High Purity Metal Powder
Selecting optimal high purity powders entails matching application requirements to material properties:
Table 6: High purity metal powder selection guidelines
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Desired material properties | Strength, corrosion resistance, conductivity, magnetism |
| Bedrijfsomstandigheden | Temperatures, pressures, stresses |
| Target component design | Geometries, precision needs |
| Production method specifications | Particle sizes, size distribution, flow characteristics |
| Purity levels mandated | Based on contamination risks and impact |
| Supplier qualifications | Quality certifications, testing capabilities |
| Budget beperkingen | Balance performance needs with costs |
- Collaborate with powder producers early when developing new applications.
- Validate claims of purity levels and properties through rigorous testing.
- Leverage suppliers’ technical expertise in tailoring materials.
Careful consideration of multiple factors helps select ideal high purity powders for specific uses.
Installing and Handling Hoogzuivere metaalpoeders
Special precautions must be taken when storing ultra-high purity powders to preserve contamination-free state:
Table 7: High purity metal powder handling guidelines
| Activiteit | Procedure | Apparatuur |
|---|---|---|
| Transport | Moisture-proof and drop-proof packaging | Double sealed containers |
| Opslag | Inert gas filled sealed gloves boxes | Vacuum storage chambers |
| Behandeling | Negative pressure glove boxes, automated systems | Load locks, isolation systems |
| Verwerking | Closed mode reactors and furnaces | Vacuum or inert gas environments |
| Bewerking | Stringent protocols minimizing exposure | Enclosed CNC mills, lathes |
- Minimize oxygen and moisture exposure to avoid oxidation.
- Ensure no cross-contamination from other materials.
- Automate handling procedures as much as possible.
Maintaining ultra-clean environments is imperative when working with high purity metal powders.
Comparing Metal Powders for Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing holds enormous promise for producing high performance components, leveraging ultra-high purity metal powders:
Table 8: Comparing metal powders for additive manufacturing
| Parameter | Nickel Powders | Titaanpoeder | Aluminiumpoeder |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kosten | Hoger | Hoogste | Lowest |
| Mechanische eigenschappen | Ductile, moderate strength | Extremely strong and light | Light, low strength |
| Thermische eigenschappen | Resistant to ~1000°C | Resistant to ~600°C | Resistant to ~400°C |
| Corrosieweerstand | Hoog | Uitstekend | Gematigd |
| Toepassingen | Ruimtevaartonderdelen, gereedschap | Aerospace structures, medical implants | Automotive parts, consumer products |
| AM Process Compatibility | Compatible with all major processes | Limited to DED and PBF only | Compatible with all major processes |
- Nickel offers best balance of performance and capabilities.
- Titanium excels where strength-to-weight ratio is critical.
- Aluminum suits cost-sensitive applications despite limitations.
Material choice depends on balancing critical component requirements with production economics.
High Purity Metal Powder Market Outlook
Global demand for ultra-high purity powders is projected to grow substantially driven by rising adoption in sophisticated technologies:
Table 9: Growth drivers for high purity metal powder market
| Factor | Contribution | Industrie |
|---|---|---|
| Miniaturization of electronics | Higher conductivity powders needed | Consumer gadgets, aerospace systems |
| Expanding additive manufacturing | Enables complex component fabrication | Ruimtevaart, medisch, automobiel |
| Rising alloy grades | Require raw metals with <10 ppm impurities | Superalloys for extreme environments |
| Investment in R&D | Enables evaluating more materials and applications | Academia, government labs |
- Market predicted to reach around $500 million by 2030.
- High purity cobalt, titanium, nickel leading growth.
- USA, Europe, China leading production and consumption.
Consistent demand from exacting industries sustains the market for contamination-free ultra-high purity metal powders.
Challenges With Hoogzuivere metaalpoeders
While possessing enormous potential, some inherent challenges exist with handling these materials:
Table 10: Challenges associated with high purity metal powders
| Probleem | Beschrijving | Matigingsstrategieën |
|---|---|---|
| Kosten | Require substantial investments in infrastructure and processing | Develop economies of scale as adoption increases |
| Verontreiniging | Risk degradation of desired properties | Follow stringent handling protocols |
| Safety hazards | Flammability, explosivity, toxicity concerns | Precautions for containment, PPE |
| Waste handling | Recover used powder without pollution | Methods for purification and reuse |
| Lack of Standards | Varying methods to demonstrate purity levels | Harmonize testing protocols globally |
Technical and economic barriers exist, but are being actively addressed allowing greater access to these specialized powders.

FAQ
Q: What level of purity is considered “high” for metal powders?
A: Generally 99.9% or higher purity signifies contamination-free high purity metal powders. Some ultra-high purity grades go up to 99.999% (5N) or more.
Q: Does high purity translate to higher powder costs?
A: Yes, costs are substantially higher than conventional metal powders due to specialized production methods required. Prices increase exponentially with higher purity levels.
Q: How to assess the actual purity of purchased metal powders?
A: Rigorously test incoming raw material lots using methods like ICP-MS chemical analysis to verify claimed purity certifications from suppliers.
Q: Does particle shape/morphology matter for high purity powders?
A: Spheroidal powders are typically preferred for ease of flow and density. Irregular shapes make handling and processing more difficult.
Q: How are high purity metal powder manufacturers improving capabilities?
A: Investments in technologies like chemically-driven powder synthesis allow lower contamination levels. Automation increases consistency.