Overzicht van 3d printen van titaniumpoeder
Titanium is a strong, lightweight, corrosion-resistant metal that is ideal for 3D printing complex geometries for aerospace, automotive, medical, and other demanding applications. Titanium powder can be used to print full-density metal parts with excellent mechanical properties using powder bed fusion technologies like selective laser melting (SLM) and electron beam melting (EBM).
This article provides a comprehensive guide to 3d printing titanium powder covering composition, properties, specifications, applications, pros/cons, suppliers, costs, and more.

Samenstelling van 3d printen van titaniumpoeder
Titanium powder for additive manufacturing consists almost entirely of the element titanium. However, small amounts of other elements like aluminum, vanadium, iron, oxygen, nitrogen and carbon can be present.
Titanium Grades for Powder Bed Fusion
| Cijfer | Samenstelling |
|---|---|
| Ti 6Al-4V | 90% titanium, 6% aluminum, 4% vanadium |
| Ti 6Al-4V ELI | Same as Ti 6Al-4V but with lower limits for interstitial oxygen, iron and nitrogen |
| Commercially Pure Titanium Grade 1 | 99.2% Minimum Titanium |
| Commercially Pure Titanium Grade 2 | 99.5% Minimum Titanium |
| Commercially Pure Titanium Grade 3 | 99.8% Minimum Titanium |
| Commercially Pure Titanium Grade 4 | 99.9% Minimum Titanium |
Ti 6Al-4V is the most common grade used in additive manufacturing today due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, weldability, and corrosion resistance. The ELI variant has improved ductility and fracture toughness.
Commercially pure titanium grades have lower strength but better biocompatibility for medical implants. Grade 5 titanium with higher oxygen content is generally not used for powder bed fusion.
Eigenschappen van 3d printen van titaniumpoeder Onderdelen
3D printed titanium parts can achieve properties similar to or exceeding traditionally manufactured titanium, with the added benefit of design freedom.
Mechanische eigenschappen
| Eigendom | Ti 6Al-4V | Ti 6Al-4V ELI | CP Ti Grade 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Treksterkte | 930 – 1050 MPa | 860 - 965 MPa | 345 – 485 MPa |
| Opbrengststerkte | 825 – 890 MPa | 795 – 875 Mpa | ≥ 275 MPa |
| Verlenging bij breuk | 8 – 15% | ≥10% | 20% |
| Vermoeidheid Sterkte | ≥ 400 MPa | ≥ 550 MPa | 275 – 550 MPa |
| Breuktaaiheid | 55 – 115 MPa√m | ≥ 100 MPa√m | N.V.T. |
3D printed titanium has stiffness, hardness and wear resistance comparable to traditional titanium manufacturing methods. Post-processing like hot isostatic pressing (HIP) can further improve material properties.
Voordelen
- Hoge sterkte-gewichtsverhouding
- Corrosieweerstand
- Biocompatibility and osseointegration
- Design freedom for topology optimization
- Minder afval vergeleken met subtractieve methoden
- Conformal cooling channels enable performance gains
Beperkingen
- High reactivity with oxygen makes handling difficult
- Print defects like porosity can reduce fatigue life
- Expensive powder material and recycling challenges
- Post-processing may be required to achieve material specs
Specificaties van 3d printen van titaniumpoeder
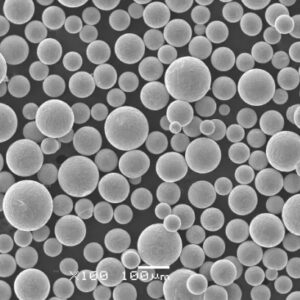
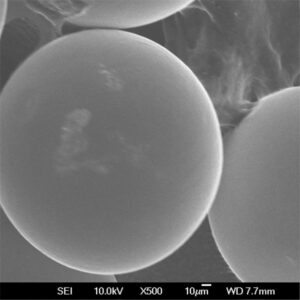
Titanium powder used for additive manufacturing needs to meet exacting standards for particle size distribution, morphology, chemistry, and other attributes.
Grootteverdeling
| Parameter | Typische waarde | Rol |
|---|---|---|
| Bereik deeltjesgrootte | 15 – 45 micron | Determines minimum feature resolution, powder spreadability |
| D10 | 20 microns | Indicates finer powder fraction |
| D50 | 30 microns | Median particle size |
| D90 | 40 microns | Indicates larger particles |
| Schijnbare dichtheid | 2,7 g/cc | Packed density of powder bed, affects reproducibility |
The powder should have a near-spherical morphology with few satellites for smooth powder spreading. Chemistry must conform to grade specifications with low impurity levels.
Other Critical Attributes
- Vloeibaarheid
- Residual oxygen and nitrogen content
- Apparent and tap density consistency
- Recycleerbaarheid
- Chemical compatibility with process
- Handling characteristics
Meeting stringent quality requirements for each parameter is critical for defect-free builds.
Toepassingen van 3d printen van titaniumpoeder
3D printing expands the design freedom of titanium, driving adoption across industries like:
Lucht- en ruimtevaart
- Structural brackets
- Lightweight lattices
- Motoronderdelen
Automobiel
- Motor sports gear
- Customized parts
Medisch en tandheelkundig
- Orthopedische implantaten
- Chirurgische instrumenten
- Patient-specific prosthetics
Olie en gas
- Corrosion-resistant valves
- Customized pipe fittings
Consumentenproducten
- Sportuitrusting
- Watch cases
- Eyeglass frames
Optimized topology and conformal cooling enables performance gains in many titanium printed parts.
Suppliers of 3d printing titanium powder
Most titanium powder suppliers offer Ti 6Al-4V grade tailored for additive manufacturing. Some also provide custom alloy design services.
Major Titanium Powder Companies
| Bedrijf | Aangeboden rangen | Diensten |
|---|---|---|
| AP&C | Ti 6Al-4V, Ti 6Al-4V ELI | Custom alloy development |
| Tekna | Ti 6Al-4V, Ti 6Al-4V ELI | Advanced plasma spheroidization |
| Timmerman additief | Ti 6Al-4V, Ti 6Al-4V ELI | Extensive QA testing |
| Praxair | Ti 6Al-4V | Nitrogen atomization |
| Epoch | Commercially Pure Titanium | Small quantity orders |
Many 3D printer OEMs like EOS and SLM Solutions also offer associated titanium powders. Recycled powders are lower cost but have higher impurity levels.
Titanium Powder Cost
| Cijfer | Morfologie | Prijsbereik |
|---|---|---|
| Ti 6Al-4V | Bolvormig | $350-$1000 per kg |
| Ti 6Al-4V ELI | Bolvormig | $500-$2000 per kg |
| CP Ti grade 1-4 | Onregelmatig | $100-$500 per kg |
Cost depends significantly on order volume, quality, supplier margins, and recycling.
Voor- en nadelen van 3d printen van titaniumpoeder
Advantages of Titanium 3D Printing
- Uitstekende mechanische eigenschappen
- High biocompatibility
- Corrosion and heat resistance
- Low density enables lightweight designs
- Design freedom for topology optimization
- Faster turnaround of custom parts
- Reduced waste compared to machining
Disadvantages of Titanium 3D Printing
- Titanium powder is expensive
- Reactivity causes handling challenges
- Porosity defects can limit fatigue strength
- Post-processing may be required
- Recycling powder has contamination risks
- Limited supplier base for aerospace quality
With continual improvements in technology, productivity and quality, 3D printing enables titanium use cases not feasible by other methods.
Comparison of Titanium Print Processes
Powder bed fusion technologies like selective laser melting (SLM) and electron beam melting (EBM) are predominantly used to 3D print titanium today.
Selectief lasersmelten (SLM)
- Higher resolution and surface finish
- Faster build speeds possible
- Limited build chamber size
Elektronenbundelsmelten (EBM)
- Builds fully dense parts in vacuum
- Uitstekende mechanische eigenschappen
- Larger build volumes possible
- Slower build speed than SLM
Gerichte energiedepositie (DED)
- Repairs existing components
- Adds features to cast or forged parts
- Combination of 3D printing and machining
- Higher porosity than powder bed methods
Each process has advantages and trade-offs for titanium printing. Hybrid manufacturing combining processes provides flexibility.
Standards for Titanium Powder and Printed Parts
Quality standards continue evolving with the rapid pace of metal additive manufacturing advancement. Some key standards include:
- ASTM F2924 – Standard specification for additive manufacturing titanium-6 aluminum-4 vanadium with powder bed fusion
- ASTM F3001 – Standard specification for additive manufacturing titanium-6 aluminium-4 vanadium ELI (extra low interstitial) with powder bed fusion
- ASTM F3184 – Standard specification for additive manufacturing stainless steel alloys by powder bed fusion
- ISO/ASTM 52921 – Standard terminology for additive manufacturing
These voluntary consensus standards help define acceptance criteria for critical powder and as-printed part attributes. User part qualification per application remains vital.

FAQ
What is the best titanium alloy for 3D printing?
Ti 6Al-4V is currently the most common titanium alloy powder used for additive manufacturing due to its excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance combined with commercial availability. Ti 6Al-4V ELI provides improved fracture toughness.
What methods can 3D print titanium parts?
Selective laser melting (SLM) and electron beam melting (EBM) are the major powder bed fusion technologies used for printing titanium. Directed energy deposition (DED) methods are also capable but have more porosity.
Does titanium need supports when 3D printing?
Yes, titanium requires supports during printing because it solidifies quickly. Carefully optimized supports are needed to avoid surface defects and wasting material while still providing adequate anchoring.
Is it cheaper to 3D print or machine titanium?
For one-off custom parts, 3D printing titanium is often cheaper since there is no tooling required. For mass production, CNC machining titanium can have a lower per part cost but has higher upfront setup expenses and material waste.
What industries use 3D printed titanium parts?
Aerospace is the largest adopter of titanium printing today thanks to buy-to-fly ratio improvements on complex components. Medical, automotive, oil and gas, sporting goods, and consumer sectors also leverage 3D printed titanium.
How much does titanium powder for 3D printing cost?
Titanium powder can range from $100-2000 per kilogram depending on composition, quality, order quantity, and other factors. Ti 6Al-4V and Ti 6Al-4V ELI spherical powders for critical applications command premium pricing over $500/kg.
What are some examples of 3D printed titanium parts?
3D printing enables innovative titanium parts like airframe brackets, turbines, motorsports components, customized prosthetics, conformally-cooled injection molds, and even eyewear or jewelry leveraging complex lattice designs.